10G Network Upgrade Between Office Buildings

Highlight
✔ Office networks have relied on lower bandwidth solutions to transfer data between buildings, which leads to slower transfer speeds and bottlenecks.
✔ Upgrading to a 10G network enables the efficient operation of video conferencing tools, online collaboration platforms, and massive data storage.
✔ By using 10G media converters and SFP+ modules, you can easily upgrade to 10G speeds without replacing all the network equipment.
Background
The company experienced significant data congestion and slow connectivity between their main headquarter and a remote office. Their existing network infrastructure was outdated and could not keep up with the increasing demands of their growing business operations, resulting in frequent data latency issues and hampering efficient workflow. They needed a solution that would provide faster and more reliable connectivity between their buildings to improve productivity and collaboration among employees.
Challenges
Upgrading the network infrastructure between office buildings can present several challenges. The company relies more on cloud computing and real-time collaboration in their new office, so the need for faster data transfer became evident. However, their existing network (2.5G) cannot handle higher speeds, resulting in potential data loss or latency. Additionally, the cost of replacing all the existing network equipment can be prohibitive.
Moreover, the distance from their headquarter to the new office is approximately 900 meters, which is far beyond the max. transmission distance supported by Ethernet cables, i.e. 100 meters or 328ft. Traditional copper-based solutions may suffer from signal degradation over long distances.
Another challenge is the need for a reliable and secure network. The company is dealing with sensitive data, so wireless solutions were not an option due to security concerns, as wireless signals can be intercepted and compromised. Therefore, it becomes imperative to find a wired solution capable of handling bandwidth-intensive tasks without compromising on speed or latency.
Solution: 10G Fiber Media Converters
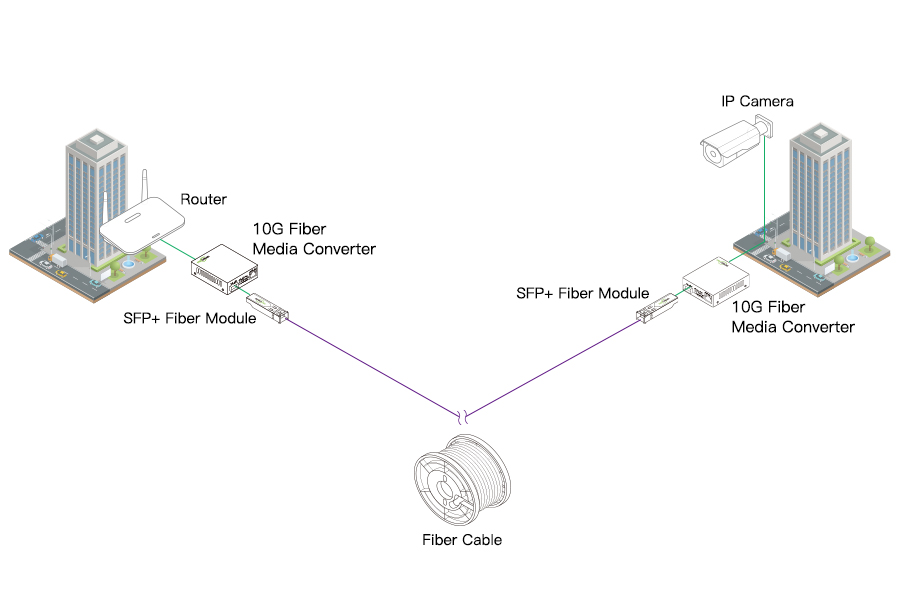
One of the most effective and budget-friendly ways to upgrade their existing network infrastructure is by using a 10G media converter. It is a device that can convert the signals between copper and fiber optic cables, allowing for high-speed data transfer over long distances, suitable for larger office complexes or buildings further apart.
With a 10G media converter, the network can achieve speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second, allowing for faster and more efficient data transfer between office buildings. This enhanced bandwidth ensures that employees can perform data-intensive tasks such as video conferencing, cloud computing and data backup, without experiencing bottlenecks or slowdowns.
Moreover, it eliminates the need to replace all the existing network equipment as they are compatible with various network interface cards and switches, significantly reducing costs associated with a complete network overhaul. While upgrading a network may sound expensive, a 10G network will eventually pay off in the long run. By investing in the right equipment, businesses can avoid frequent upgrades or additional investments to accommodate increasing bandwidth demands.
How to Install a 10G Network Between Two Buildings?
Building a 10G point-to-point fiber optic network between two buildings requires careful planning and installation. First, we need to gather the necessary equipment for the setup:
10G Media Converters: These devices convert electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa. Choose a pair of converters that support 10G connectivity.
BiDi SFP+ Modules: These modules are used to interface with the media converters, and they enable bi-directional communication on a single fiber.
Pre-terminated Fiber Cables: These cables come with connectors already attached, saving installation time and effort.
Fiber Enclosures and Patch Panels: These hardware items provide protection and organization for the fiber connections.
Secondly, plan the path for the fiber cables, avoiding obstacles and potential sources of interference. Consider both underground and aerial routes, taking into account any required permits or approvals for trenching or cable installation. Place conduit or innerduct if necessary, for protection and easy future maintenance. Then, carefully lay the fiber cables along the planned route, making sure to leave some slack at each end for termination.
Thirdly, install the 10G media converters in their designated locations, and insert the BiDi SFP+ modules into the SFP slots of the media converters. Next, connect one end of the fiber cable to the SFP+ module on each media converter. Take extra care to avoid bending or stressing the fiber cable during connection.
Lastly, connect the 10G media converters to a power source
and power them up. Use appropriate network testing equipment, like an optical
time-domain reflectometer (OTDR), to measure signal loss and verify the
integrity of the fiber connection.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Topology